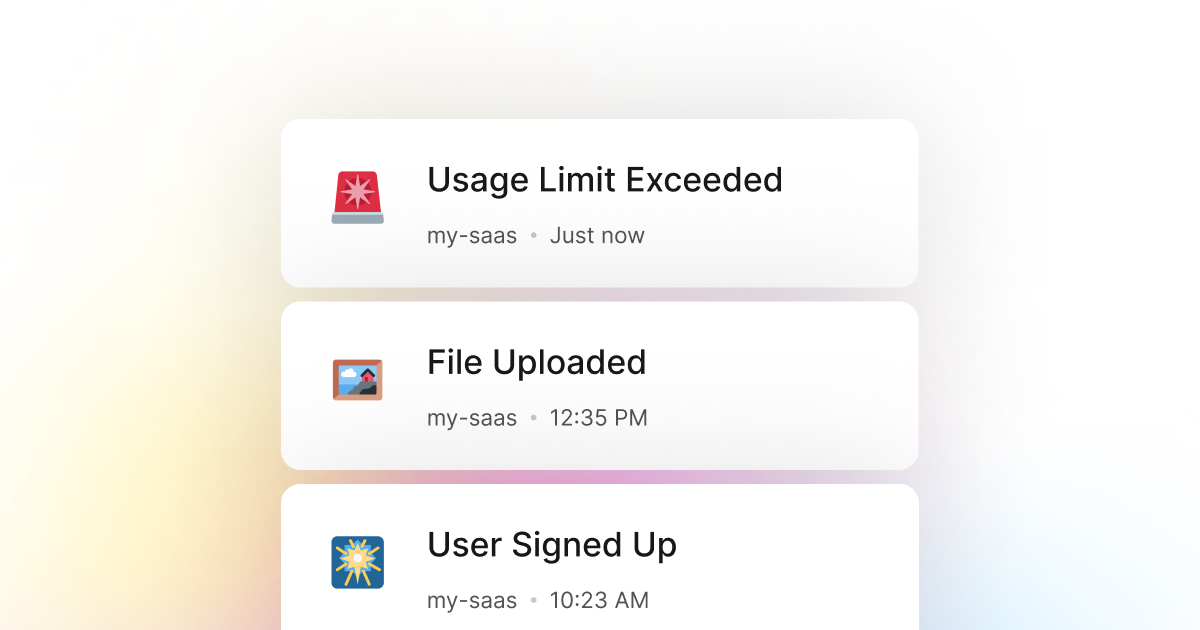
These days, a lot of services are moving to a pay-as-you-go model. This model is either based on a monthly usage limit or metered usage. This is especially common for cloud, software, and other online services. So, chances are that if you're building a service with NodeJs, you'll have to roll your usage model and limits.
No matter your implementation, you will be required to set up an internal system to track usage and notify yourself and your team when a user has reached their limit. This is a common enough problem as it helps you understand how your users use your service, and you can improve your product based on that.
LogSnag is a service that helps you monitor your important events in real-time. It's an excellent tool for this problem and works seamlessly with NodeJs. In addition, LogSnag makes it trivial to send events to your dashboard and receive push notifications when something important happens.
For example, let's say you're building a service with NodeJs that allows users to upload files. However, you want to limit the number of files a user can upload to 10. You can use LogSnag to send an event to your dashboard when a user uploads a file. You can then set up a rule to notify you when a user has uploaded ten files. This way, you will know when a user has reached their limit, allowing you to take further action if needed.
Setting up LogSnag
- Sign up for a free LogSnag account.
- Create your first project from the dashboard.
- Head to settings and copy your API token.
NodeJs code snippets
Copy the following code snippet to your NodeJs project. Please note that you will need to replace the API token with your own.
Using NodeJs with Axios
Using NodeJs with Native
Using NodeJs with Request
Using NodeJs with Unirest
NodeJs integration details
LogSnag is a flexible and easy-to-use event tracking service that works excellently with NodeJs. In addition to real-time event tracking and cross-platform push notifications, LogSnag provides powerful user journey tracking, simple event filtering, search, and analytic tools such as charts.
In addition to tracking usage events, you can also use LogSnag to track other important events such as errors, user sign-ups, user logins, payments, or anything else you can think of.
Setting up LogSnag with your NodeJs application takes a few minutes, and you can start tracking events in no time.
Other use-cases for LogSnag
- Monitor your CI/CD build status for your NodeJs application
- Monitor your CPU usage in your NodeJs application
- Monitor when database goes down in your NodeJs application
- Monitor high disk usage in your NodeJs application
- Monitor when a user changes their email address in your NodeJs application
- Monitor failed logins in your NodeJs application
- Monitor failed payments for your NodeJs application
- Monitor memory usage in your NodeJs application
- Monitor MySQL downtime in your NodeJs application
- Monitor when a new feature is used in your NodeJs application
- Monitor your Postgres downtime in your NodeJs application
- Monitor Redis downtime in your NodeJs application
- Monitor suspicious activity in your NodeJs application
- Monitor when a user is being rate limited in your NodeJs application
- Get a notification when your NodeJs code is done executing
- Send push notifications to your phone or desktop using NodeJs
- Track canceled subscriptions in your NodeJs application
- Track your NodeJs cron jobs
- Track when a file is uploaded to your NodeJs application
- Track when a form is submitted to your NodeJs application
- Track payment events via NodeJs
- Track user sign in events in NodeJs
- Track user signup events via NodeJs
- Track waitlist signup events via NodeJs