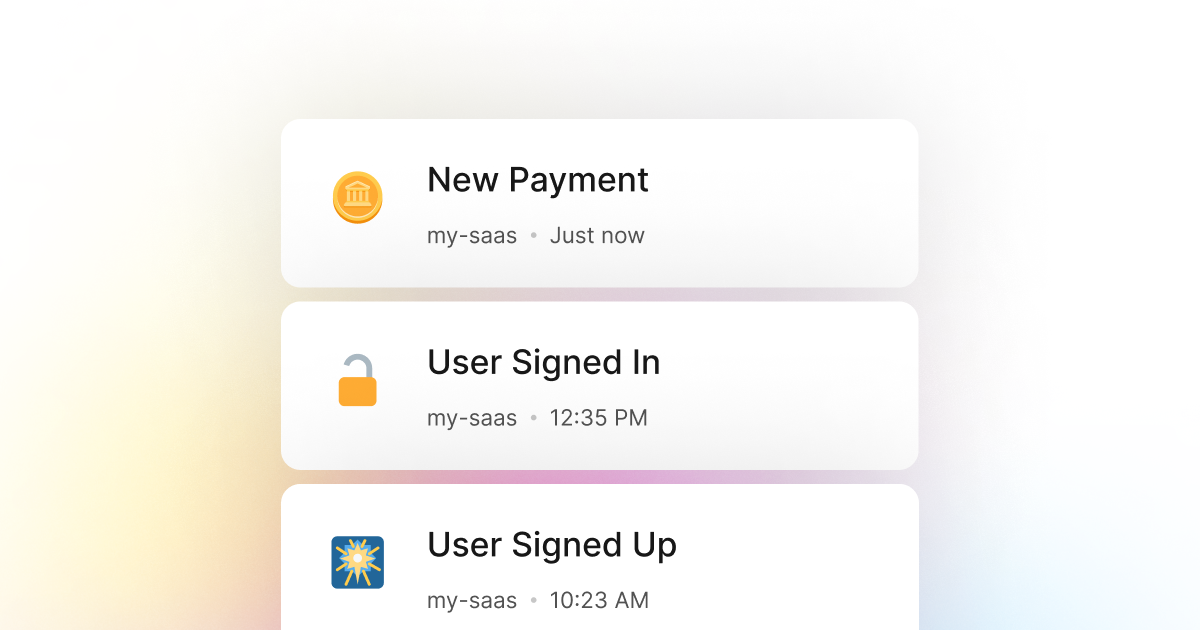
Most of the time, when building a Python product that requires users to authenticate and sign in to access the product, you may decide that it is essential to track the sign-in attempts.
Monitoring the sign-in events is an excellent way to track the number of users who continue to log in and use your Python application. This is a great way to gauge the effectiveness of your product and measure your user retention rate.
A good understanding of this metric is critical to the success of a product. It can give you great insight into how your business grows and how your users interact with your Python product.
An easy way to set up event tracking is to use LogSnag, a simple event tracking tool that works seamlessly with Python.
Start monitoring user sign-in events
- Sign up for a free LogSnag account.
- Create your first project from the dashboard.
- Head to settings and copy your API token.
Python code snippets
All you have to do next is to copy the following code snippets into your Python code and replace the YOUR_API_TOKEN and project values with your API token and project name.
Using Python with http.client
Using Python with Requests
Python integration details
LogSnag is a simple event tracking tool that works seamlessly with Python and makes it easy to track almost anything in your Python code.
LogSnag allows you to track your important events in real-time and create timelines of your events. It also makes it easy to create custom metrics and charts such as the number of sign-in attempts per day, the conversion funnels for users who sign up and sign in, and other such metrics.
You may also create simple or complex user journeys for tracking and monitoring individual user journeys through your product.
LogSnag is also available on desktop, mac, iOS, and Android and allows you to receive real-time updates and push notifications when your users sign in, sign out, or use your product.
Other use-cases for LogSnag
- Monitor your CI/CD build status for your Python application
- Monitor your CPU usage in your Python application
- Monitor when database goes down in your Python application
- Monitor high disk usage in your Python application
- Monitor when a user changes their email address in your Python application
- Monitor failed logins in your Python application
- Monitor failed payments for your Python application
- Monitor memory usage in your Python application
- Monitor MySQL downtime in your Python application
- Monitor when a new feature is used in your Python application
- Monitor your Postgres downtime in your Python application
- Monitor Redis downtime in your Python application
- Monitor suspicious activity in your Python application
- Monitor when a user exceeds the usage limit for your Python service
- Monitor when a user is being rate limited in your Python application
- Get a notification when your Python code is done executing
- Send push notifications to your phone or desktop using Python
- Track canceled subscriptions in your Python application
- Track your Python cron jobs
- Track when a file is uploaded to your Python application
- Track when a form is submitted to your Python application
- Track payment events via Python
- Track user signup events via Python
- Track waitlist signup events via Python